Device Management Updates from WWDC 2020: What Mac Admins Need to Know
 Kandji Team
Kandji Team
Every year, Apple releases all of its major device management updates at its Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC) event — and WWDC 2020 has been packed with big news.
In this article, we’re going to break down some of the biggest announcements that came out of the conference. Here’s a quick overview of what we’ll cover:
- macOS Big Sur: Device Management Changes
- New macOS Security Features
- iOS & iPadOS: Device Management Changes
- New iOS & iPadOS Security Features
macOS Big Sur: Device Management Changes
At WWDC, managing Apple devices got a lot of attention, but one of the biggest device management updates involved deploying and managing macOS Big Sur at scale. In this section, we’re going to cover all of the device management highlights before taking a look at new security features for Mac devices.
In this post, we are only covering these items at a high level. If you're looking for a deep dive on everything that's new with macOS Big Sur, read our post: macOS Big Sur & MDM: The Comprehensive Guide for Mac Admins.
macOS Automated Device Enrollment
Apple has rolled out the latest iteration of macOS with continued support for the latest device management (MDM) features, like Automated Device Enrollment. With this enrollment method, all the user needs to do is boot up their Mac devices, select a language, and connect to a Wi-Fi network.
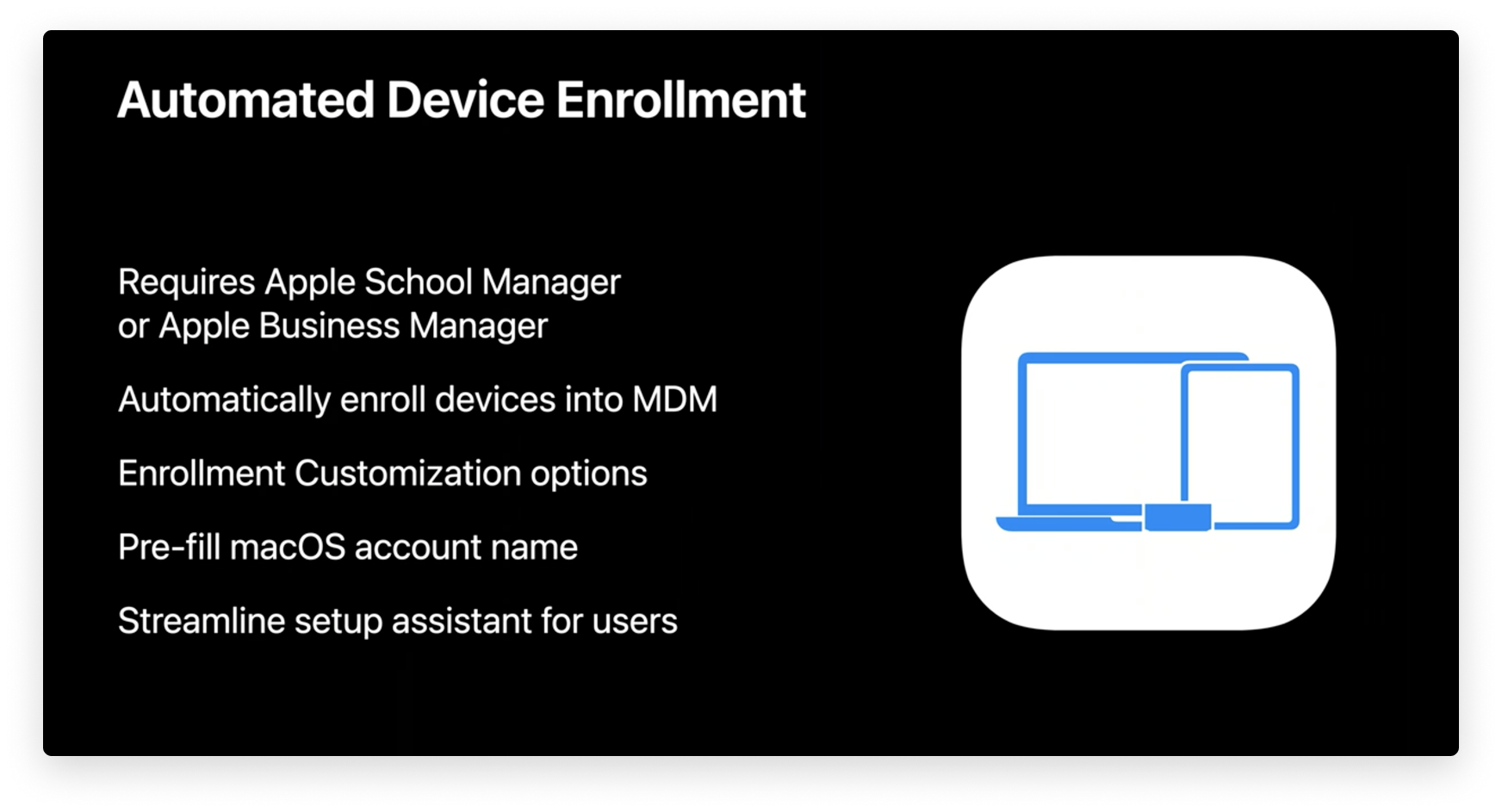
Image source: developer.apple.com
From there, company-owned Mac devices are automatically enrolled in the company’s MDM solution. That means IT administrators won’t have to touch the devices to set them up manually, and users can start using their new Mac devices sooner.
Using Enrollment Customization gives IT even more power over the enrollment process. This new feature lets IT add custom branding, consent text, and modern authentication to their teams during the setup period.
Using Enrollment Customization with your Identity Provider (IdP), IT can provide a better user experience while using modern authentication methods (such as Microsoft Azure Active Directory, Okta, Ping, and more) by auto-filling full name and short name credentials in the “Create a Computer Account” page.
IT administrators can further streamline the setup assistant by choosing which steps are hidden or shown to users, such as Siri, Touch ID, FileVault Disk Encryption, Analytics, Location Services, and more.
All-in-all, using Automated Device Enrollment is a great way to simplify MDM enrollment for company-owned devices, even letting you remotely supervise devices during activation and lock MDM enrollment for ongoing management. You can find more information on setting up and using Automated Device Enrollment in the relevant section of our guide to Apple device enrollment methods.
Auto Advance Comes to Mac
A few years ago, Apple introduced a feature that streamlined setting up Apple TV at scale — and now, they’re bringing it to the Mac. Using the Auto Advance feature, users just have to plug in a Mac to power and ethernet cords, and then turn it on.

Image source: developer.apple.com
Once the Mac starts, it will automatically skip all setup screens, bringing the user directly to the login page. This is by far the fastest way to set up a Mac, and you can still customize the setup process to meet your company’s needs.
To use Auto Advance, you’ll need to manage your devices using Apple Business Manager, and while only power and ethernet are required, your network must support DHCP. If you use encrypted disks, you’ll be required to enter your password.
Lights Out Management for the Mac Pro
We also got some news about managing the Mac Pro at WWDC. Managing Apple devices at scale has always been a fixture of these conferences, but WWDC 2020 introduced a really exciting new feature called Lights Out Management.
With Lights Out Management (LOM), IT administrators can remotely startup, shutdown, and reboot one or more Mac Pro devices — even if they’re unresponsive. This is made possible by sending a command from your MDM solution to the MDM controller on your Mac network.
This involves enrolling a Mac to act as a LOM controller on your local network, and then enrolling all of your Mac Pro devices to that controller. Once this is done, when you send a command to your MDM server, the LOM controller will receive and distribute it to all of your Mac Pro devices.
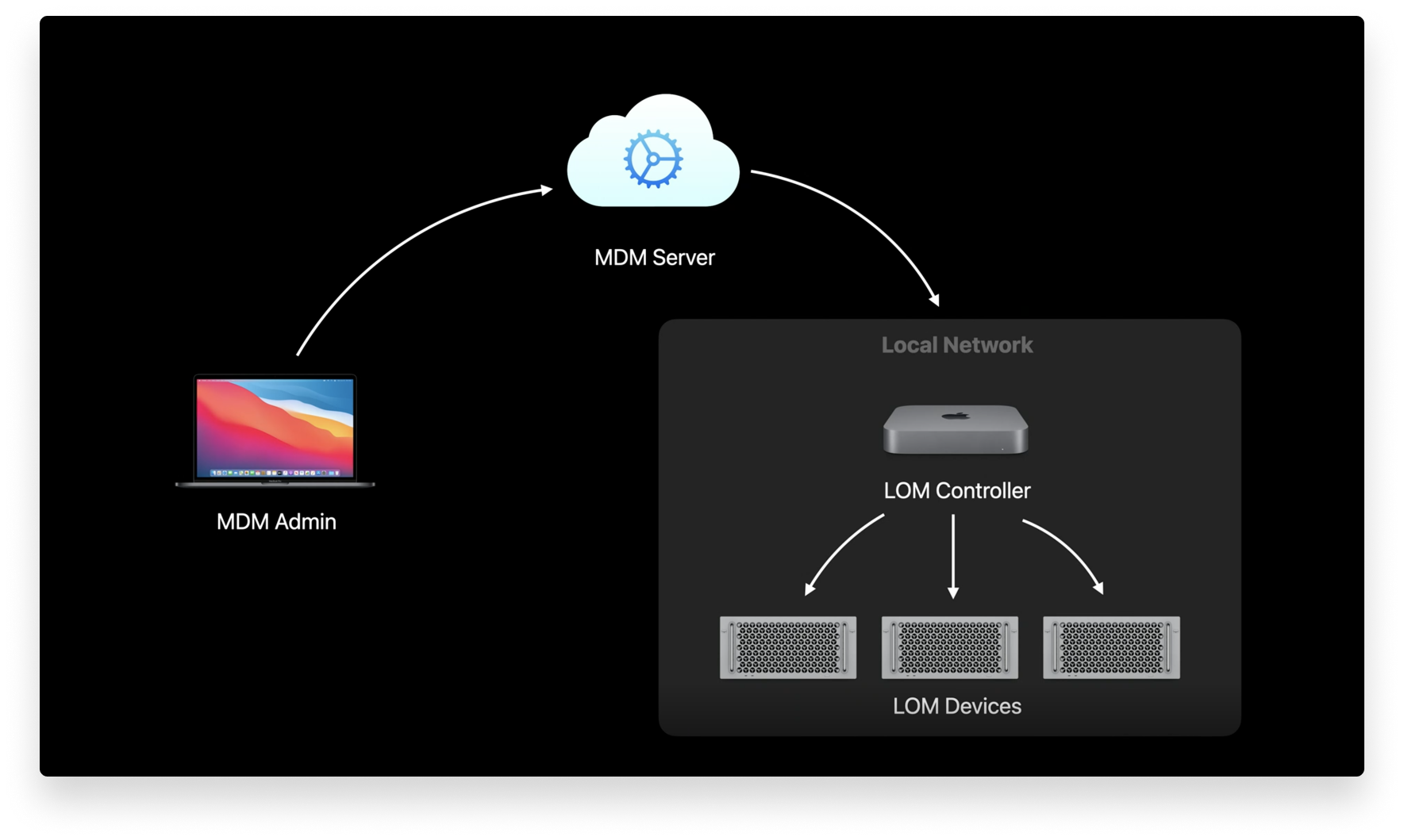
Image source: developer.apple.com
There are three requirements to use Lights Out Management:
- You need macOS Big Sur on your Mac Pro devices.
- Your Mac Pro devices must be on the same subnet over IPv6.
- You must install the Lights Out Management payload.
Changes to Device Supervision
When an Apple device is supervised, IT administrators can exercise more control over it, letting them automate actions, add restrictions, and do things like bypass activation lock, install apps “silently,” push OS updates remotely, or filter web content.
In WWDC 2020, this changed. Apple announced that any Mac enrolled in User-Approved MDM will be considered supervised. Before this change, Mac devices enrolled in User Approved MDM didn’t have the same capabilities as those enrolled via Automated Device Enrollment.

Image source: developer.apple.com
Now, IT administrators will have the same management capabilities for Mac devices enrolled in User-Approved MDM, such as controlling activation locks, using bootstrap tokens, querying and deleting local users, replacing and removing profiles, installing supervised restrictions to profiles using MDM commands, and scheduling software updates.
Managed Software Updates
At WWDC 2020, Apple also announced new MDM commands for software updates. Among them is the ability to force Mac users to accept software updates and then restart, and also to defer non-OS updates and major releases of macOS for up to 90 days.
Changes have also been made to increase security, such as the removal of the software update catalog and the removal of the Ignore Flag for major OS updates.
Mac Gets Managed Apps

Image source: developer.apple.com
While previously only available for iOS, at WWDC 2020 Apple introduced Managed Mac Apps. This new feature will let IT administrators remove apps with MDM commands or have apps removed upon device un-enrollment. Managed Mac Apps also support iOS-style app configuration and feedback, and IT can use MDM commands to convert eligible unmanaged apps into Managed Apps. However, Managed App conversion isn’t supported for user-enrolled devices.
New Content Caching MDM Command
Apple released content caching for Mac a few years ago in an attempt to speed up download rates and reduce Internet usage with Mac apps, books, iCloud content, software updates, Xcode components, and more. Now, content caching supports a wide range of data types, and it even supports Internet recovery. The Internet recovery feature doesn’t include the initial boot image, but the recovery image is cached so you can restore Mac devices on your network quickly.
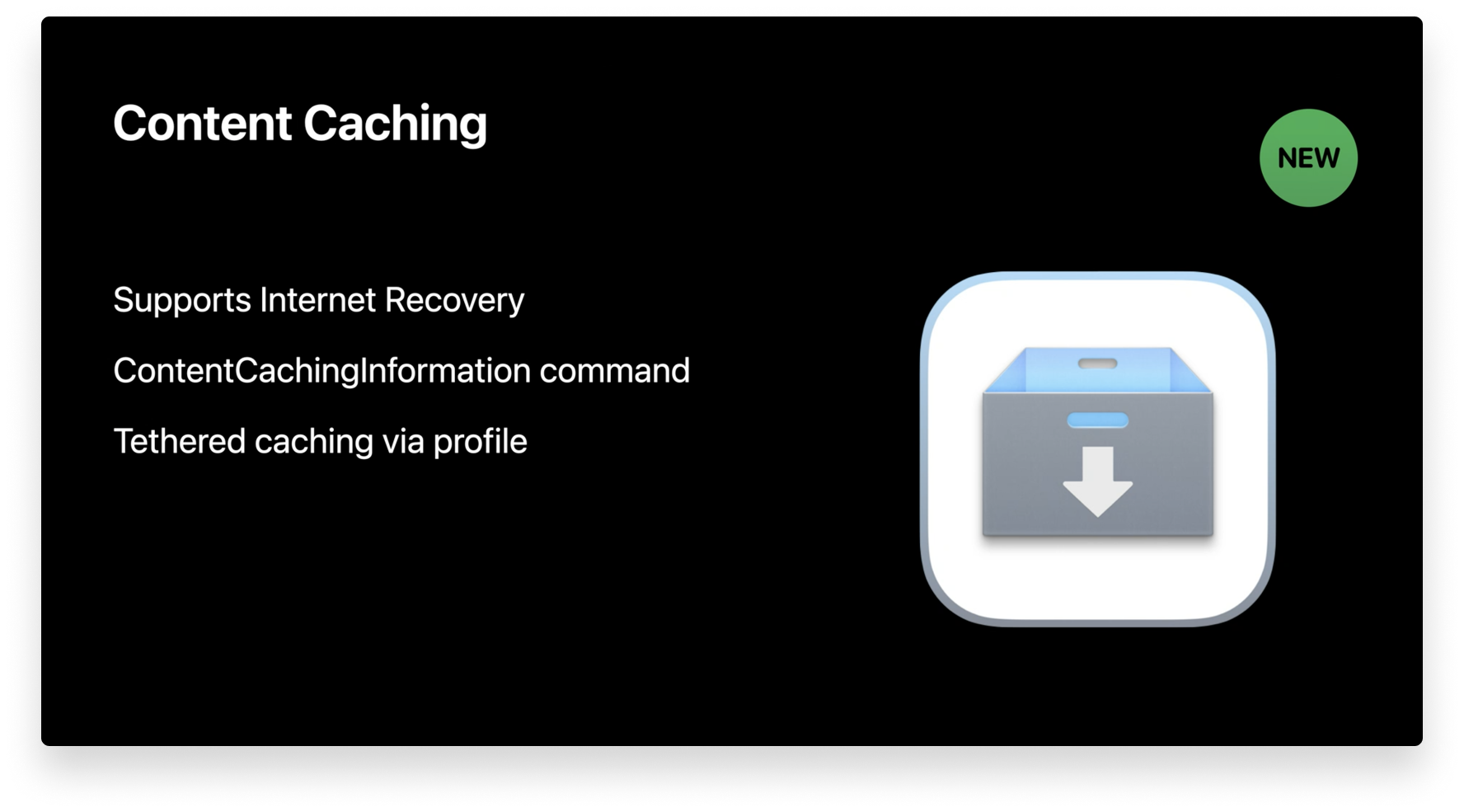
Image source: developer.apple.com
When content caching was introduced to macOS, Apple released a new tab in Activity Monitor that displayed important performance metrics. At WWDC 2020, Apple announced that those metrics are now available via the new ContentCachingInformation MDM command. This will help IT determine if content caching is in use, gauge how it’s being used, and help users download apps faster.
New Security Features Come to Mac
Bootstrap Token
At WWDC 2020, Apple announced that Bootstrap Tokens are now required to approve and load Kernel Extensions (KEXTs) via MDM on future Apple Silicon devices running macOS Big Sur. This means IT won’t be able to complete tasks like installing updates via MDM without a Bootstrap Token on these future devices.
Now with Bootstrap Tokens on macOS Big Sur, IT no longer has to create complicated workflows to grant SecureToken attributes to macOS accounts. Before macOS Big Sur, Bootstrap Tokens could only be used to grant SecureToken to network accounts and Auto Admin accounts created via MDM. Now, Bootstrap Tokens can automatically grant SecureToken to any local account when it signs into the Mac computer.
Bootstrap Tokens were introduced in macOS Catalina as encryption keys provided to an MDM server. They previously only assisted with enabling SecureToken for mobile network accounts or the Auto Admin account. Now with macOS Big Sur, Bootstrap Tokens will be leveraged to grant every user SecureToken when they sign in (this applies only if they sign in graphically), not just network accounts or the Auto Admin.
Secure Token will be granted to the first account whose password is set. This excludes an Auto Admin account as the password for that account is set using a hash via MDM, and when creating a Secure Token, macOS requires the password to be available in plain text. Auto Admins can still be granted secure token simply by signing into the account graphically.
Another important reminder of a change made in macOS Catalina 10.15.4 is that macOS will automatically attempt to generate and escrow a Bootstrap Token to MDM anytime a Secure Token enabled user signs in.
Preventing Accidental Profile Installation
Apple has taken measures to prevent users from accidentally installing configuration profiles. The ability to download profiles was introduced in iOS and iPadOS. However, in order to install the profile, the user must download it and then manually install it via System Preferences. Because profiles can configure devices, it’s important that they only come from trustworthy sources, so this extra measure ensures that users do not accidentally install profiles.
The same downloaded profiles capability is now available in macOS. When a user downloads a profile, a notification will prompt them to review it in Settings. They can visit the Profiles section to review the new profile, where they will have the option to delete or install it.
Preventing Silent Profile Installation from Command Line
Apple also introduced security measures to prevent silent profile installs at WWDC. Managing Apple devices requires limiting dangerous actions that users may accidentally perform. As of macOS Big Sur, profiles can no longer be completely installed using Terminal. If a user attempts to install a profile using the Command Line, it will be treated as a downloaded profile, requiring a visit to Settings to complete the installation.
Network Setup Limitations for Standard Users
macOS Big Sur also includes new features for an existing tool called networksetup. The networksetup tool makes it easier to view and edit network settings using Terminal. While previously, standard users and admins had the same capabilities to view and edit network settings from the Command Line, now each account type has its own abilities.

Image source: developer.apple.com
Standard users no longer have the same level of control over networksetup as admins. Now, standard users are limited to reading network settings, turning Wi-Fi power on or off, and changing the Wi-Fi access point. Admins still have full capabilities.
New Randomized Serial Numbers
In order for Automated Device Enrollment to know which devices to enroll upon activation, it uses device serial numbers. These are unique twelve-character strings of numbers and letters that contain information about when and where a device was built, along with the device’s identification code.
This information helps Apple ensure product quality, but it can also be used maliciously. So, Apple announced a new serial number at WWDC 2020. Now, completely random ten-character serial numbers are being issued to devices. Third-party programs will need to be able to support the old and new serial number format moving forward.
iOS & iPadOS: Device Management Changes
Apple Configurator Apps & Books Locations
Apple Configurator helps IT administrators configure iPhones, iPads, and AppleTVs using a USB cable. Apple announced at WWDC 2020 that Apple Configurator now supports Apps & Books Locations. These Locations, which are provided by Apple Business Manager, can refer to different places within an organization where devices use different Apps and Books.
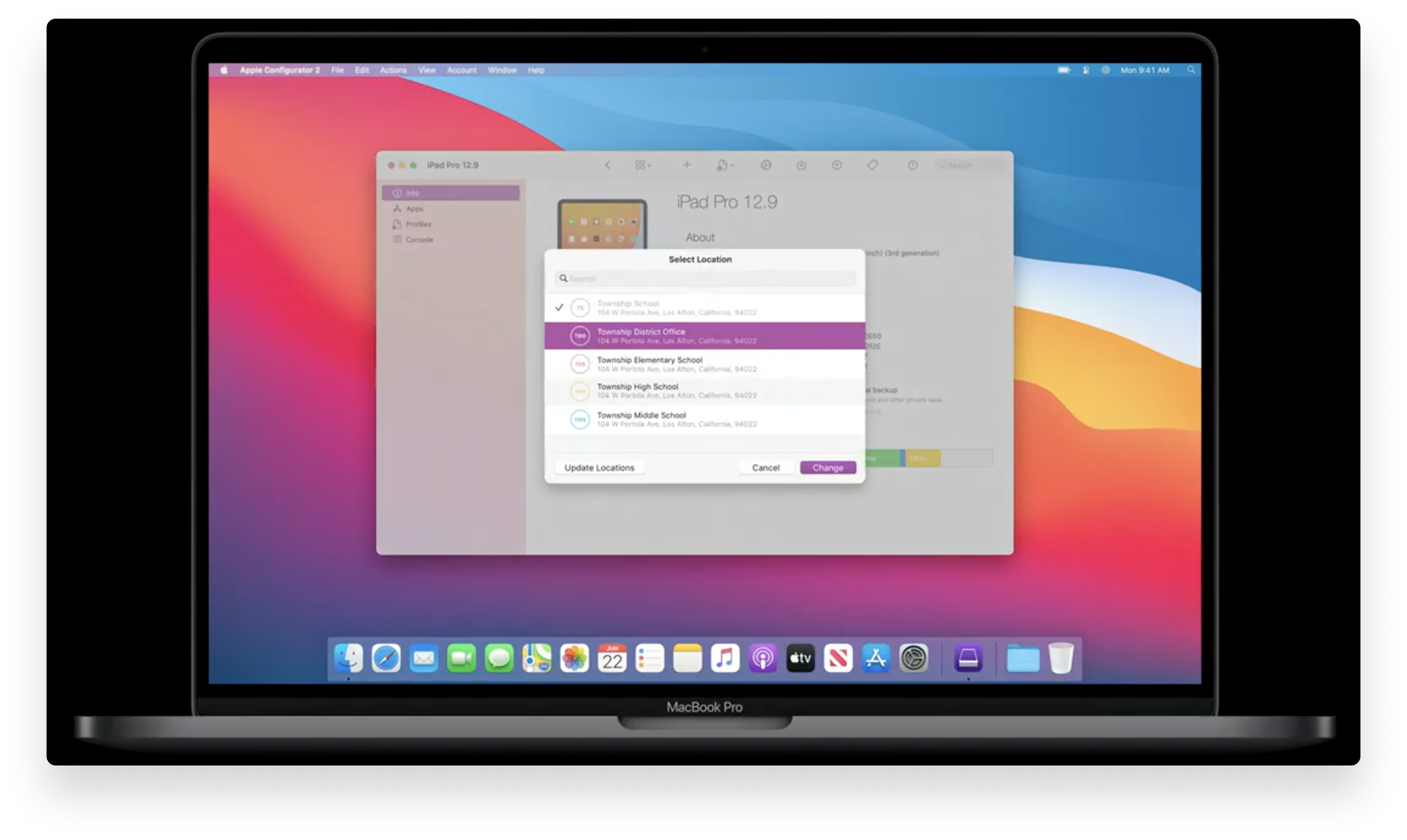
Image source: developer.apple.com
IT administrators can now go to the Account menu and select the Location they want to use. This will display a unique collection of Apps and Books for each Location that has been configured in Apple Business Manager.
Setup Assistant Skip Keys
Apple has released the setup assistant payload for iOS. To use the payload, IT administrators will specify the skip keys they used in Automated Device Enrollment, which will take effect in future upgrades.
This payload will let you skip setup assistant pages during an upgrade that you didn’t know about when you were initially setting up a device. Skipping these pages is now possible on all supervised devices, not just those enrolled using Apple Business Manager.
Shared iPad for Business
Shared iPad is a new feature for iPadOS that can give users a personal experience on a shared device. Previously only available for education customers, Shared iPad can now be used for businesses by leveraging Apple Business Manager and their MDM solution. (For a deep dive on this, read our guide to Shared iPad for business.)
Employees can sign into the shared device using their Managed Apple ID, and if you use Microsoft Azure AD as your IdP, users can sign in using federated authentication. (You can read more about this in our guide to federated authentication.)
Shared iPad also supports dynamic numbers of cached users, so you can set the amount of storage for each user — rather than just a fixed number of users. IT administrators can also now delete all users at once, and sign in for temporary sessions. This lets users use the device without creating an account.
Non-Removable Managed Apps for iOS
Previously, IT administrators could prevent users from deleting apps by locking the home screen. While this ensured that users never deleted vital business apps, it took away some personalization for users.
Now, IT can mark critical apps as non-removable, while allowing users to rearrange, delete, and install other apps. If a user tries to remove a non-removable app, the user will be alerted that it cannot be done.
Managed Notification Previews
To prevent sensitive data from being shared, Apple announced at WWDC 2020 a new control for notification previews. This is a new key in the notification settings payload called Preview Type, which controls when notifications are shown (always, when unlocked, or never). This is only available on supervised devices.
Set Timezone MDM Command
Image source: developer.apple.com
When managing remote devices in multiple countries, defaulting to your MDM server’s timezone can cause a lot of problems, like authentication issues. This is why Apple introduced the new Set Timezone MDM command at WWDC 2020. This new command lets IT administrators choose the timezone for each device.
New Security Features Come to iOS
Per-Account VPN for iOS
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) let people safely send and receive data across public networks. Previously, iOS supported three types of VPN: Full Tunnel (for all traffic), Split Tunnel (for specific traffic), and Per App VPN (for certain app data).
Apple announced Per Account VPN at WWDC 2020, which lets IT administrators choose which VPN accounts should use. This can be used to choose replacement VPNs for Contacts, Calendars, and Mail domains, and it can also associate accounts with VPNs (much like Per App VPN).
Encrypted DNS
Another big announcement from WWDC 2020 was encrypted DNS. While most user communication with servers is encrypted, communication with DNS servers is often not secure. With encrypted DNS, that changes, letting developers enhance security without configuring a VPN. This can now be managed via MDM.
Randomized MAC Addresses
As of iOS 14, devices use randomized MAC addresses when associating with Wi-Fi networks. If a device fails to join the network, it will revert back to its hardware MAC address. This setting can be disabled by users in Settings, or it can be disabled in the wifi payload.
At this year’s WWDC, managing Apple devices took up a lot of the spotlight. The whole team here at Kandji is excited to continue to support new features within our MDM solution so you can get the most out of your Apple fleet. With powerful features like zero-touch deployment, one-click compliance, and offline remediation, Kandji has everything you need to enroll, configure, and secure your devices.

